projects

Our projects
Large areas of globally important tropical peatland in Southeast Asia are under threat from land clearance, degradation and fire jeopardising their natural functions as reservoirs of biodiversity, carbon stores and hydrological buffers. Local research capability will be strengthened enabling peatland managers to better understand and address the different, interrelated processes operating in tropical peatlands.
- Sambodja Lestari, BOS Foundation in ...
- LiDAR-Data and 30 RGB-Photos from Bukit ...
- RGB Photos from Block C and Sabangau catchment ...
- LiDAR survey 2011 in Central and East Kalimantan ...
- Three Ortho-Photo-Mosaiks taken with ...
- LiDAR and Ortho-Photo Survey in East- and Cenral ...
- LiDAR-Survey in Central Kalimantan for CKPP in ...
- EU - Project: RESTORPEAT-Project: Restoration of ...
- EU - Projekt: STRAPEAT-Seminar / Workshop on the ...
- EU Project - The STRAPEAT Project sponsored by ...
- EU Project: - Natural Resource Functions (Interim ...
- EU Project: - NATURAL RESOURCE FUNCTIONS, ...
- Mega Rice Project - The Benefits of Space-Based ...
- Mega Rice
gallery

image gallery
Find a large collection of images from many years of exploration by kalteng-consultants.
History Borneo - Kalimantan · Excursions to peatland 1996 · Mega Rice Project 1999 · 2004 · 2005 · 2006 · 2007 · 2008 · 2009 · 2010 · 2011 · 2012 · 2013 · 2014 · 2015 · 2016-March · 2016-August ·
projects
EU Project: - Natural Resource Functions (Interim Report), BIODIVERSITY AND SUSTAINABLE MANAGEMENT OF TROPICAL PEATLANDS
for the EEC INCO Project; Contract No: ERB IC18-CT98-0260; called EUTROP; 2-1999
1999_Natural_Resource_Functions Interim-Report
The overall aim of this Kalteng Consultants research programme (started in 1995) is an investigation into the evolution and the economic potential of the peat swamp forest (P.S.F.) resource in Central Kalimantan by remote sensing techniques.
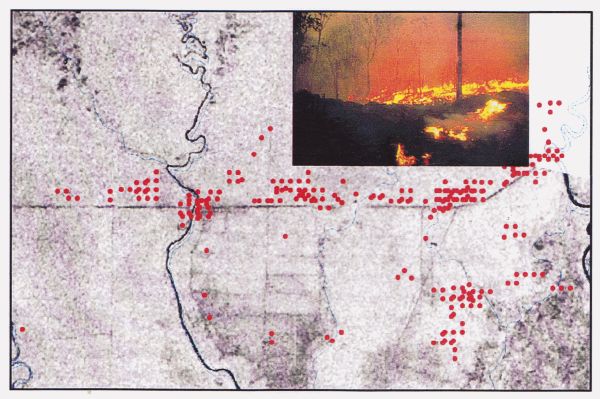
A multispectral and multitemporal image analysis has been used to monitor the environmental importance and agricultural potential as well as wildlife conservation aspects. This report gives information's about field trails to Central Kalimantan in March 1997 and in June and Nov. 1998. The natural vegetation of most tropical peatland is rain forest containing trees of commercial value, e.g. Ramin. Selective forestry is probably the most sustainable use of this resource, but it is also the principal loser when more destructive developments take place.
The current status of forestry on tropical peatland needs to be determined, especially the different categories of designation, e.g. production forest, conversion forest, protection forest together with the policies which govern these and control logging and other activities. A land-use conversion 1 Million ha (Mega)-Rice-Project for rice cultivation including transmigration was started by the Indonesian government with a feasibility study and, in April 1996, with the digging of the irrigation channels into the peat swamp. The development of an area of one million hectares in Central Kalimantan, situated between the Rivers Sebangau in the west, River Kahayan, River Kapuas and River Barito in the east and the Java Sea in the South is planned and partly realised. The total area of impact is 1.4 million hectares for the Blocks A, B, C, D and E. The project faces problems of peat domes with a height up to 10m between the main rivers. Satellite-images of the heavy forest fires in Autumn 1997 in Central Kalimantan has been processed too. To undertake global monitoring/survey in a short time, it was essential to use LANDSAT Thematic Mapper, SPOT and ERS1/2 Radar images, linked to a programme of field checking of forest, peatland development and peat condition. Remote sensing technology was used for all survey, monitoring and planning tasks. This paper presents some of the results from LANDSAT, SPOT, ERS1 and ERS2 image processing activities from aerial surveys on 13 and 27 June and 3 November 1998, as well as from several ground truth campaigns in 1997 and 1998 (compare ref. 2 Kalteng report from 1996). Between 1995 and 1998 this area of Kalteng was visited 7 times . All data will be evaluated for the preparation of a detailed peatland analysis to be stored in a Geographical Information System (GIS). This evaluation will take place in the next three years (1999 - 2001) within the framework of an European Union project with 6 international partners. See page: EU Project