remote sensing

our work
kalteng remote sensing shows trends in environments like Kalimantan.
- TanDEM-X elevation model data for canopy height ...
- Monitoring Forest Threats with C- and L-band SAR, ...
- Ground Penetrating Radar Mapping of Peat ...
- Spectral Variability and Discrimination ...
- Kalteng Consultants Company Profile, Oct
- Visiting of Wetlands International Camp on ...
- Ortho Photo Mosaik von Kelurahan Tumbang Tahai ...
- Ortho-Photo Mosaik from Lake Batu, north of ...
- International Symposium & Workshop on Tropical ...
- The Contribution of CHRIS/PROBA Data for Tropical ...
- Workshop on Spatial Planning and new Remote ...
- Ortho-Photo Generation and Mosaiking of City ...
- Ortho-Photo Mosaik from Kecamatan Bukit Batu, ...
- International Workshop, Wild Fire and Carbon ...
- Planning Group for Kecamatan Bukit Batu gathered ...
- Carbon Storage in the Northern Sabangau Area ...
- Peat Land Topography derived from 30m Resolution ...
- Peat depth, minerals below peat, carbon, fires ...
- Carbon Storage in the Northern Sebangau Area ...
- Peatland Topography DEM-measurements with ...
- Precise Measurements of Peatland Topography and ...
- Environmental Management Study of the Tangkiling ...
- Environmental Field Trials and GIS Image ...
- Land Cover Change on Peatland in Kalimantan ...
- The Impact of Logging and Land Use Change in ...
- Tracks along the Kalimantan Highway from Kasongan ...
- Fires in 2002 monitored on the Landsat-images 14 ...
- The Amount of Carbon released from Peat and ...
- Land use Change in Central Kalimantan over the ...
- Remote Sensing and Aerial Survey of Vegetation ...
- Monitoring land cover and impacts, Remote Sensing ...
- Fire Impacts and Carbon Release on Tropical ...
- Ecological Impact of the one Million Hectare Rice ...
- Land Use Change and (Il)-Legal Logging in Central ...
- Peat fires in Central Kalimantan, Indonesia: Fire ...
- Environmental Helicopter Flight Trails with ...
- Impact of the 1997 Fires on the Peatlands of ...
- Application of Remote Sensing and GIS to monitor ...
- Monitoring of 1997/1998 Fires and Burnt Scars in ...
- Flight survey over the Mega Rice Project and over ...
- Application of Remote Sensing and GIS to survey ...
- Mega Rice Project in Central Kalimantan, ...
- Satellite Images and Aerial Photos from the ...
- The need for better
- Remote Sensing Verification by Aerial Surveys and ...
- NATURAL RESOURCE FUNCTIONS, BIODIVERSITY AND ...
- Excursion to Central Kalimantan, ...
- Satellite Images and Aerial Photography’s from ...
- Symposium of International Peat Society, ...
- Indonesia Travel to Jakarta, Bali and Kalimantan ...
- The Mega Rice Project Central Kalimantan ...
- Land Use Planning and Environmental Monitoring in ...
- Bildverarbeitung von Sensorbildern zur Erstellung ...
- GIS-Workshop, Camp km48 Sangai.
- Monitoring Land Use Change on Tropical Peatland ...
- Seminar on Scientific Implications of the ...
- Report of Ground Truth Campaigns incl. Aerial ...
- Ground and Helicopter verification of Satellite ...
- Environmental Detection from Satellite and ...
- First visit to Central Kalimantan in June 1995, ...
- Environmental Helicopter with Modular Sensor ...
- Remote Sensing with a Thermal Imager on an ...
- The Use of an Environmental Helicopter for the ...
- EUROMAR-SEASTARS a Modular Multi-Sensor System ...
gallery

image gallery
Find a large collection of images from many years of exploration by kalteng-consultants.
History Borneo - Kalimantan · Excursions to peatland 1996 · Mega Rice Project 1999 · 2004 · 2005 · 2006 · 2007 · 2008 · 2009 · 2010 · 2011 · 2012 · 2013 · 2014 · 2015 · 2016-March · 2016-August ·
remote sensing
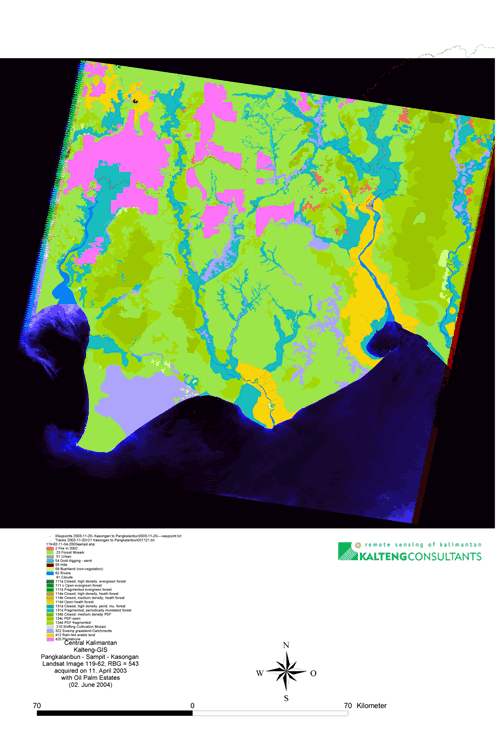
Land Cover Change on Peatland in Kalimantan Indonesia between 1999 and 2003; 6-2004
Landsat image 119-61+62 web/kt/dyn/pdf_files/kalteng 2004-272 BOEHM TAMPERE 04.04.2004.pdf presented at
12th International Peat Congress under the topic "Wise use of Peatlands"
in Tampere, Finland on 6 - 11. June 2004
by H.-D.V. Boehm
Kalteng Consultants,
Kirchstockacher Weg,
D-85635 Hoehenkirchen, near Munich, Germany,
Tel: +49-8102-774848, Fax: +49-8102-774850,
Email: viktorboehm@t-online.de
Summary / Abstract
Vast areas of peat swamp forest (PSF) cover the coastal plains of Central Kalimantan from the coast of the Java Sea to the provincial capital of Palangka Raya, to Sampit, to Pangkalanbun and further North. PSF is among the earth's most endangered ecosystem, with a huge carbon storage capacity, extremely fragile to disturbance. Several Landsat ETM images 118-61, 118-62 (2003 only), 119-61 and 119-62, acquired between 1999 and 2003, were compared using detailed multi-temporal analysis. These images show major changes in this largest remnant of tropical peatland related to extreme rates of deforestation, the worst fires in 2002, since 1997. Of the 5.6 million hectare land around Sampit, 4.8 million hectare were processed, 2.5 million hectare for 1999 and 2003. It was found that oil palm plantation (Elaeis guineensis) between Palangkanbun and Sampit increased by more than 50 % from approx. 143,000 ha 5.7% in 1999 to 218,000 ha 8.7% in 2003. In the West of the Katingan river there are many places with small-scale gold mining in quartz-sand.
With the establishment of the Mega Rice Project (MRP), many people were able to enter the previously inaccessible interior of this peatland landscape, exploit residual timber resources, mostly on an illegal basis, and using fire for land clearance as the most economical method. During the El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO) in 1997 and 2002, many of these fires spread to open forest areas and continued to burn with great intensity, than also burning the peat below the vegetation and releasing large amounts of carbon. The minor el Nino of 2002 led to human health problems, although somewhat less serious than in 1997. Our analysis suggests that previous legal logging prepared the ground for further degradation of forests by fire, illegal logging and oil palm farming. The different blocks from MRP were analysed and classified with the Landsat images taken on 15 Feb. 2003, after the 2002 fires, which covered in average 16.2% (227,000 ha) in the 1.4 million hectare blocks A, B, C, E, E2, E3 and E4. Block B had with 35.7% the largest amount of burn scars. If this situation continues there is a high risk of most peat swamp forest of Central Kalimantan being destroyed within a few years. This would have grave consequences for the local hydrology, climate, biodiversity and livelihood of local population. Keywords: Central-Kalimantan, Tropical Peatlands + PSF, Oil palm estates, Remote Sensing + GIS, Peat-Fires
Landsat image 119-62