remote sensing

our work
kalteng remote sensing shows trends in environments like Kalimantan.
- TanDEM-X elevation model data for canopy height ...
- Monitoring Forest Threats with C- and L-band SAR, ...
- Ground Penetrating Radar Mapping of Peat ...
- Spectral Variability and Discrimination ...
- Kalteng Consultants Company Profile, Oct
- Visiting of Wetlands International Camp on ...
- Ortho Photo Mosaik von Kelurahan Tumbang Tahai ...
- Ortho-Photo Mosaik from Lake Batu, north of ...
- International Symposium & Workshop on Tropical ...
- The Contribution of CHRIS/PROBA Data for Tropical ...
- Workshop on Spatial Planning and new Remote ...
- Ortho-Photo Generation and Mosaiking of City ...
- Ortho-Photo Mosaik from Kecamatan Bukit Batu, ...
- International Workshop, Wild Fire and Carbon ...
- Planning Group for Kecamatan Bukit Batu gathered ...
- Carbon Storage in the Northern Sabangau Area ...
- Peat Land Topography derived from 30m Resolution ...
- Peat depth, minerals below peat, carbon, fires ...
- Carbon Storage in the Northern Sebangau Area ...
- Peatland Topography DEM-measurements with ...
- Precise Measurements of Peatland Topography and ...
- Environmental Management Study of the Tangkiling ...
- Environmental Field Trials and GIS Image ...
- Land Cover Change on Peatland in Kalimantan ...
- The Impact of Logging and Land Use Change in ...
- Tracks along the Kalimantan Highway from Kasongan ...
- Fires in 2002 monitored on the Landsat-images 14 ...
- The Amount of Carbon released from Peat and ...
- Land use Change in Central Kalimantan over the ...
- Remote Sensing and Aerial Survey of Vegetation ...
- Monitoring land cover and impacts, Remote Sensing ...
- Fire Impacts and Carbon Release on Tropical ...
- Ecological Impact of the one Million Hectare Rice ...
- Land Use Change and (Il)-Legal Logging in Central ...
- Peat fires in Central Kalimantan, Indonesia: Fire ...
- Environmental Helicopter Flight Trails with ...
- Impact of the 1997 Fires on the Peatlands of ...
- Application of Remote Sensing and GIS to monitor ...
- Monitoring of 1997/1998 Fires and Burnt Scars in ...
- Flight survey over the Mega Rice Project and over ...
- Application of Remote Sensing and GIS to survey ...
- Mega Rice Project in Central Kalimantan, ...
- Satellite Images and Aerial Photos from the ...
- The need for better
- Remote Sensing Verification by Aerial Surveys and ...
- NATURAL RESOURCE FUNCTIONS, BIODIVERSITY AND ...
- Excursion to Central Kalimantan, ...
- Satellite Images and Aerial Photography’s from ...
- Symposium of International Peat Society, ...
- Indonesia Travel to Jakarta, Bali and Kalimantan ...
- The Mega Rice Project Central Kalimantan ...
- Land Use Planning and Environmental Monitoring in ...
- Bildverarbeitung von Sensorbildern zur Erstellung ...
- GIS-Workshop, Camp km48 Sangai.
- Monitoring Land Use Change on Tropical Peatland ...
- Seminar on Scientific Implications of the ...
- Report of Ground Truth Campaigns incl. Aerial ...
- Ground and Helicopter verification of Satellite ...
- Environmental Detection from Satellite and ...
- First visit to Central Kalimantan in June 1995, ...
- Environmental Helicopter with Modular Sensor ...
- Remote Sensing with a Thermal Imager on an ...
- The Use of an Environmental Helicopter for the ...
- EUROMAR-SEASTARS a Modular Multi-Sensor System ...
gallery

image gallery
Find a large collection of images from many years of exploration by kalteng-consultants.
History Borneo - Kalimantan · Excursions to peatland 1996 · Mega Rice Project 1999 · 2004 · 2005 · 2006 · 2007 · 2008 · 2009 · 2010 · 2011 · 2012 · 2013 · 2014 · 2015 · 2016-March · 2016-August ·
remote sensing
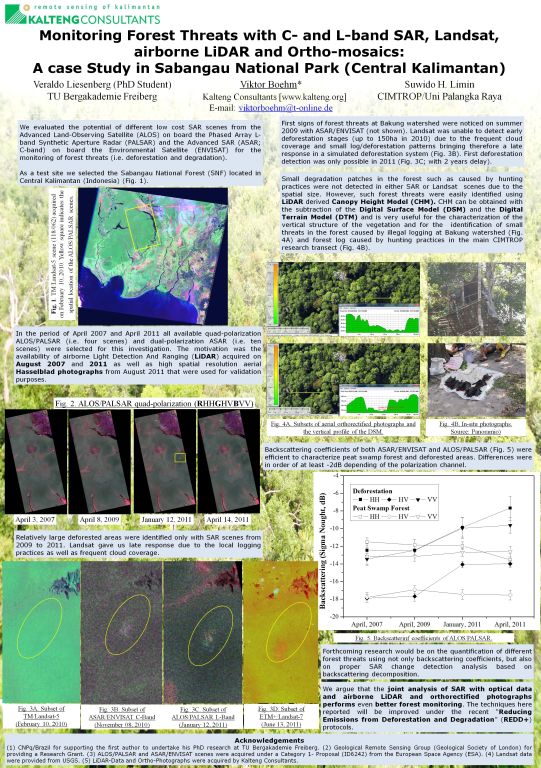
Monitoring Forest Threats with C- and L-band SAR, Landsat, airborne LiDAR and Ortho-mosics: A case Study in Sabangau National Park (Central Kalimantan)-Bogor-9-2012
by Veraldo Liesenberg1, Viktor Boehm2 & Suwido H. Limin³
1Faculty of Geosciences, Geotechnique and Mining, TU Bergakademie Freiberg, Bernhard-von-Cotta-Str. 2, D-09599, Freiberg, Germany.
2 Kalteng Consultants [www.kalteng.org], Kirchstockacher Weg 2, D-085635, Hoehenkirchen, Germany. E-mail: viktorboehm@t-online.de
3 Universitas Palangka Raya and CIMTROP, Jalan Yos Sudarso, Palangka Raya, 73112, Central Kalimantan, Indonesia.
Poster presentet at the JST-JICA Symposium in Bogor 13-14- Sept 2012
Abstract
We evaluated the potential of different low cost SAR scenes from the Advanced Land-Observing Satellite (ALOS) on board the Phased Array L-band Synthetic Aperture Radar (PALSAR) and the Advanced SAR (ASAR; C-band) on board the Environmental Satellite (ENVISAT) for the monitoring of forest threats (i.e. deforestation and degradation).
As a test site we selected the Sabangau National Forest (SNF) located in Central Kalimantan (Indonesia). In the period of April 2007 and April 2011 all available quad-polarization PALSAR (i.e. five scenes) and dual-polarization ASAR (i.e. ten scenes) were selected for this investigation. The motivation was the availability of airborne Light Detection And Ranging (LiDAR) acquired on August 2007 and 2011 as well as high spatial resolution aerial Hasselblad photographs from August 2011 that were used for validation purposes. The SAR data were multi-looked, geocoded at a spatial resolution of 30m and finally converted to backscattering coefficients. Polarimetric features, decomposition techniques and interferometric coherence were also extracted from the datasets.
Since an effective monitoring system at a regular basis does not exist in Central Kalimantan, a simulation of the presence and absence of optical Landsat according to the SAR datasets was also evaluated. Landsat images were atmospherically corrected and converted into surface reflectance. We precede with a visual interpretation over the SAR scenes taking into account the temporal changes in the backscattering coefficients and the variations of the scattering mechanism (i.e. surface or volumetric scattering). Relatively large deforested areas were identified from 2009 to 2011.
Landsat was unable to detect early deforestation stages due to the frequent cloud coverage bringing late response in a simulated deforestation system. LiDAR derived Canopy Height Model (CHM) and Intensity as well as high resolution photographs were useful for the characterization of the vertical structure of the vegetation and for the identification of small threats in the forest caused by illegal logging and hunting practices in the main CIMTROP research transect.
Small degradation patches were not detected in either SAR or Landsat scenes. We argue that the joint analysis of SAR with optical data and airborne LiDAR and orthorectified photographs performs even better forest monitoring and thus encourage the further development of joint techniques. The techniques here reported will be improved under the recent “Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Degradation” (REDD) mechanism.
Keywords: forest threats, deforestation, forest degradation, peat swamp forest monitoring, RADAR-SAR, LiDAR